
Sep 8, 2020 | Black Holes (Stellar), Cosmology, Daily Space, Exoplanets, Supermassive Black Holes
Join us today as we examine major news coming out last week from institutions analyzing data from the LIGO and Virgo gravitational wave detectors: the largest and farthest collision detected yet has led to the discovery of an “impossible” black hole. Plus a triple-star system has planetary rings and the camera that will be at the heart of the Vera Rubin Observatory takes its first images… of broccoli.
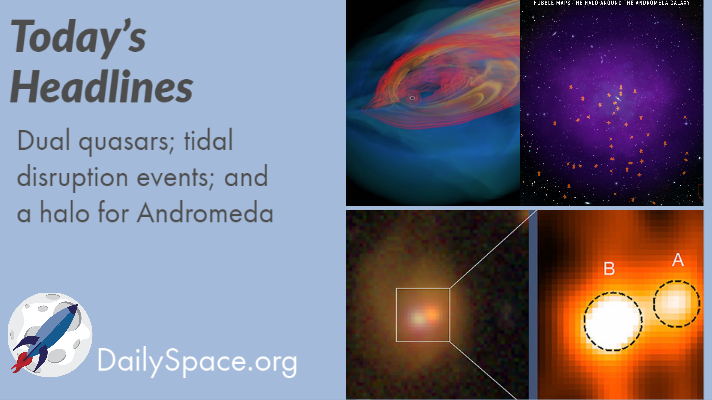
Aug 31, 2020 | Daily Space, Galaxies, Gemini North, Quasar, Supermassive Black Holes
Join us today as we examine observations for dual quasars in the process of merging and a star being torn apart by its supermassive black hole. Plus, Hubble data used to map a halo around the Andromeda galaxy.

Aug 18, 2020 | Asteroids, Daily Space, Exoplanets, Quasar
Join us today for a lot of unsatisfying news. First, two objects appear to be pulsing in gamma-rays at the same pace, but they’re 100 light years apart. Next, it turns out that stars with planets look chemically like any other star. And finally, our interstellar visitor, ‘Oumuamua, is NOT made of molecular hydrogen ice.

Aug 4, 2020 | Cosmology, Daily Space, Galaxies, Mars, Neutron Stars / Pulsars, Star Forming Region
Join us today as we talk about newly released research that suggests the waters on ancient Mars were subglacial and not free-flowing. Also, a black hole goes dormant and star formation goes wild. Meanwhile, computer models show that unequal neutron stars colliding may cause a big “bang” that can be detected on Earth.

Aug 3, 2020 | Daily Space, Galaxies, Neutron Stars / Pulsars, Our Solar System, Quantum, Stars, Supernovae Remnants, White Dwarfs
Join us today as we look at how quantum mechanics and Einstein’s theory of general relativity work together in white dwarfs. Machine learning is used to find a galaxy with an extremely low abundance of oxygen. Scientists find signs of a neutron star in supernova 1987A. And researchers managed to locate two recently arrived meteorites in Australia with the help of fireball detection cameras.

Jul 23, 2020 | Daily Space, Exoplanets, Galaxies, Supernovae, Very Large Array, White Dwarfs
Join us today as we learn that galaxies have magnetic fields, too. Also, scientists are excited to catch the ultraviolet flash of a type Ia supernova and directly image a multi-planet extrasolar system. Finally, researchers have developed a new method for finding “lost” worlds in NASA TESS data (but no dinosaurs, thankfully).








 We record most shows live, on Twitch. Follow us today to get alerts when we go live.
We record most shows live, on Twitch. Follow us today to get alerts when we go live.